Advantages Of Serial Communication Over Parallel Communication
In data transmission, parallel communication is a method of conveying multiple binary digits simultaneously. It contrasts with serial communication, which conveys only a single bit at a time; this distinction is one way of characterizing a communications link. Define serial and parallel transmission methods and discuss the advantages of. Serial transmission: data bits are sent one bit at a time over a single wire.
Definition Of Serial Transmission In Serial Transmission, data is sent bit by bit from one computer to another in bi-direction. Each bit has its clock pulse rate. Eight bits are transferred at a time having a start and stop bit (usually known as a Parity bit) i.e. 0 and 1 respectively. For transmitting data to a longer distance, data cables are used. It consists of D-shaped 9 pin cable that connects the data in series.
Serial Transmission has two subclasses synchronous and asynchronous. In asynchronous transmission, an extra bit is added to each byte so that the receiver is alert about the arrival of new data. Usually, 0 is a start bit, and 1 is the stop bit. In synchronous transmission, no extra bit is added rather the data transferred in the form of frames which contains multiple bytes. Definition Of Parallel Transmission In Parallel Transmission, various bits are sent together simultaneously with a single clock pulse. It is a fast way to transmit as it uses many input/output lines for transferring the data.
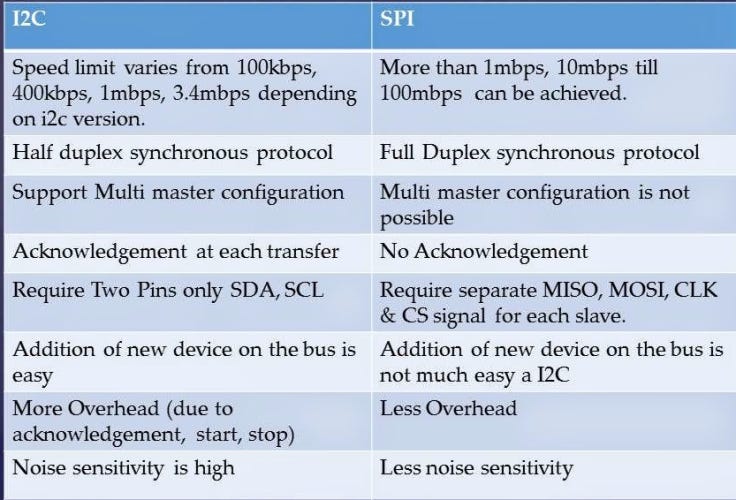
Parallel Transmission uses a 25 pin port having 17 signal lines and 8 ground lines. The 17 signal lines are further divided as • 4 lines that initiates handshaking, • 5 status lines used to communicate and notify errors and • 8 to transfer data. Key Differences Between Serial And Parallel Transmission • Serial transmission requires a single line to communicate and transfer data whereas, parallel transmission requires multiple lines. • Serial transmission used for long distance communication whereas, the parallel transmission used for shorter distance. • Error and noise are least in serial as compared to parallel transmission. Since one bit follows another in Serial Transmission whereas, in Parallel Transmission multiple bits are sent together.
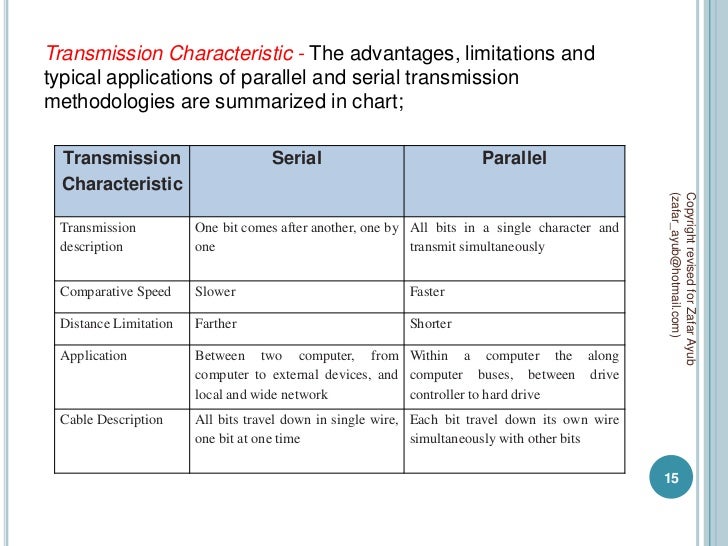
• Parallel transmission is faster as the data is transmitted using multiples lines whereas, in Serial transmission data flows through a single wire. • Serial Transmission is full duplex as the sender can send as well as receive the data whereas, Parallel Transmission is half duplex since the data is either sent or received. • Serial transmission cables are thinner, longer and economical in comparison with the Parallel Transmission cables.
• Serial Transmission is reliable and straightforward whereas, Parallel Transmission is unreliable and complicated. Conclusion Both Serial and Parallel Transmission have their advantages and disadvantages respectively. Parallel Transmission is used for shorter distance, provides greater speed. On the other hand, Serial Transmission is reliable for transferring data to longer distance.
Hence, we conclude that both serial and parallel are individually essential for transferring data.
Contoh Program Dengan Visual Foxpro 9 Full. 2010 Halo teman bagi yang hobi buat program pake Microsoft Visual Foxpro 9.0 dan blum punya master programnya gak usah. Visual foxpro 9 download.
Teach Any Computer Science Class We have put together a full GCSE Computer Science curriculum that will give you all the teaching materials you need to teach any topic. Whether you're a brand new Computer Science teacher, or you've been teaching ICT for years, our resources will save you hours and hours of lesson preparation every single week. There are two ways to transfer data between computers: Serial Transmission and Parallel Transmission. Serial Transmission Data is sent bit by bit from one computer to another in two directions. Each bit has a clock pulse rate.
Eight bits are transmitted at a time with a start and stop bit known as a parity bit, which is 0 and 1 respectively. Data cables are used when transmitting data to a longer distance. The data cable has D-shaped 9 pin cable that connects the data in series. Categories of Serial Transmission Asynchronous transmission – an extra bit is added to each byte to alert the receiver on the arrival of new data.
0 is used as a start bit while 1 used as a stop bit. Synchronous transmission – no extra bit is added to each byte. Data is transferred in batches which contains multiple bytes. Parallel Transmission Several bits are transmitted together simultaneously with one clock pulse rate. It transmits quickly as it utilizes several input and output lines for sending the data. It uses a 25-pin port with 17 signal lines and 8 ground lines. The 17 signal lines are divided as • 4 lines – initiates handshaking • 5 lines – communicates and notifies errors • 8 lines – transfers data Applications Serial transmission occurs between two computers or from a computer to an external device located some distance away.